The Enduring Appeal of the Hippie Wool Jumper: A Cultural and Fashion Analysis
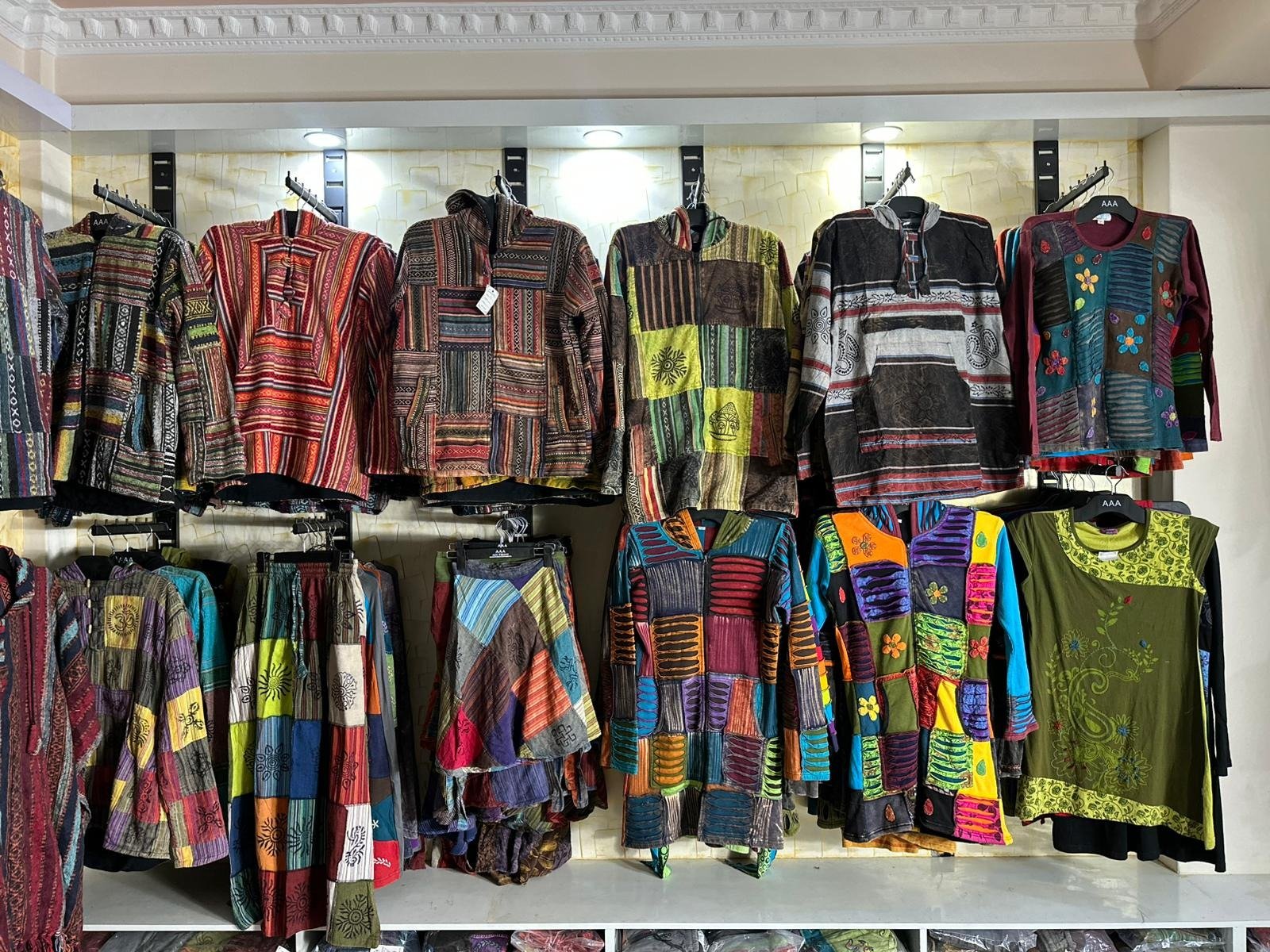

The hippie wool jumper stands as one of the most iconic and enduring pieces of counterculture fashion, representing far more than mere clothing. This distinctive garment embodies a philosophy of life, environmental consciousness, and artistic expression that continues to resonate with contemporary fashion enthusiasts and cultural movements decades after its initial emergence in the 1960s.
Table of Contents
Historical Origins and Cultural Context
The hippie wool jumper emerged during the transformative period of the 1960s counterculture movement, when traditional fashion norms were being challenged alongside social and political structures. This garment became a symbol of rebellion against mass-produced, synthetic clothing that dominated mainstream fashion. The choice to wear handcrafted wool jumpers represented a conscious rejection of consumer capitalism and an embrace of natural materials and artisanal craftsmanship.
The roots of the hippie wool jumper can be traced to various cultural influences, including folk traditions from Ireland, Peru, Nepal, and other regions where wool knitting had deep cultural significance. As young people in the 1960s sought authentic experiences and connections to traditional crafts, they adopted these garments as expressions of their values and worldview.
The association with the hippie movement wasn’t merely aesthetic; it was deeply philosophical. Wearing a wool jumper signified alignment with environmental consciousness, support for traditional craftspeople, and a preference for quality over quantity. These garments often featured earthy colors, natural dyes, and intricate patterns that reflected the wearer’s connection to nature and appreciation for handmade artistry.
Design Characteristics and Aesthetic Elements
The typical hippie wool jumper is characterized by several distinctive features that set it apart from conventional knitwear. These garments often feature oversized, relaxed silhouettes that prioritize comfort and freedom of movement over fitted, structured designs. The loose-fitting nature of these jumpers reflected the hippie philosophy of rejecting restrictive clothing that might inhibit natural body movement or self-expression.
Color palettes in hippie wool jumpers tend toward earth tones, including deep browns, forest greens, burnt oranges, and rustic reds. These colors were often achieved through natural dyeing processes using plants, roots, and minerals, further emphasizing the connection to nature and sustainable practices. Some jumpers featured vibrant, psychedelic patterns that reflected the era’s artistic experimentation and the influence of Eastern spiritual traditions.
Textural variety is another hallmark of the hippie wool jumper. Many pieces incorporated different knitting techniques, creating varied textures within a single garment. Cable knits, seed stitches, and fair isle patterns were popular choices, often combined in creative ways that showcased the knitter’s skill and artistic vision. Fringe details, tassels, and decorative elements like wooden buttons or bone toggles added to the handcrafted aesthetic.
The construction quality of authentic hippie wool jumpers was typically superior to mass-produced alternatives. Hand-knitted or crafted by skilled artisans, these garments were built to last, reflecting the movement’s values of sustainability and opposition to disposable fashion culture.
Materials and Craftsmanship
Wool selection played a crucial role in defining the authentic hippie jumper experience. Natural, unprocessed wools were preferred, often sourced from local farms or small-scale producers. Sheep’s wool remained the most common choice, but jumpers made from alpaca, mohair, and even exotic fibers like yak wool gained popularity among those seeking unique textures and properties.
The craftsmanship behind hippie wool jumpers emphasized traditional techniques passed down through generations. Many were hand-knitted by individual artisans or small cooperatives, particularly in regions like Peru, Ireland, and Nepal, where these skills were deeply embedded in local culture. This artisanal approach ensured that each jumper possessed unique characteristics and subtle variations that mass production could never replicate.
The knitting techniques employed in creating hippie wool jumpers often incorporated complex patterns and construction methods. Aran knitting from Ireland, with its distinctive cable patterns and symbolic motifs, became particularly associated with the movement. These patterns weren’t merely decorative; they carried cultural significance and told stories about the communities that created them.
Quality control in hippie wool jumper production relied on individual craftsmanship rather than industrial standards. This resulted in garments with character and personality, where slight irregularities were viewed as marks of authenticity rather than flaws. The time-intensive nature of hand-knitting meant that each jumper represented hours of skilled labor and artistic dedication.
Cultural Impact and Symbolism
The hippie wool jumper transcended its function as clothing to become a powerful symbol of cultural resistance and alternative lifestyle choices. Wearing such a garment was a form of non-verbal communication that signaled alignment with countercultural values, environmental consciousness, and rejection of mainstream consumer culture.
These jumpers became associated with various aspects of hippie philosophy, including the back-to-the-land movement, appreciation for traditional crafts, and support for small-scale, sustainable production methods. The choice to wear handcrafted wool jumpers represented a conscious decision to support artisans and traditional communities rather than large corporations.
The garment also played a role in breaking down gender barriers in fashion. The unisex nature of many hippie wool jumpers challenged traditional gender-specific clothing norms, allowing both men and women to wear similar styles without social stigma. This gender-neutral approach aligned with the broader hippie movement’s questioning of conventional social roles and expectations.
Music festivals and gatherings became important venues for displaying hippie wool jumpers, where they served both practical and symbolic functions. The warmth and comfort provided by wool made these garments ideal for outdoor events, while their distinctive appearance helped wearers identify like-minded individuals and build community connections.
Contemporary Relevance and Modern Adaptations
Today’s fashion landscape has witnessed a remarkable revival of interest in hippie wool jumpers, driven by several contemporary trends and concerns. The growing awareness of fast fashion’s environmental impact has led many consumers to seek sustainable alternatives, making handcrafted wool jumpers increasingly appealing to environmentally conscious shoppers.
Modern interpretations of the hippie wool jumper often blend traditional aesthetics with contemporary design elements. Fashion designers have incorporated classic hippie jumper features into updated silhouettes that appeal to current style preferences while maintaining the garment’s essential character and cultural significance.
The rise of the slow fashion movement has created renewed appreciation for the craftsmanship and durability that define authentic hippie wool jumpers. Consumers increasingly value garments that tell a story, support traditional crafts, and offer longevity over trendy, disposable alternatives.
Social media platforms have facilitated a renaissance in hand-knitting and traditional crafts, with young people rediscovering the satisfaction of creating their own hippie-inspired wool jumpers. Online communities share patterns, techniques, and philosophy, keeping the tradition alive while adapting it to contemporary contexts.
Economic and Social Dimensions
The production and consumption of hippie wool jumpers have significant economic implications, particularly for traditional craft communities and small-scale producers. The renewed interest in these garments has created market opportunities for artisans in developing countries where traditional knitting skills remain strong.
Fair trade organizations have embraced hippie wool jumpers as products that embody ethical production principles. These garments often provide crucial income for rural communities while preserving traditional skills and cultural practices that might otherwise disappear in the face of industrialization.
The premium pricing typically associated with authentic hippie wool jumpers reflects their true production costs, including fair wages for artisans and high-quality materials. This pricing structure challenges the artificially low costs of mass-produced fashion and educates consumers about the real value of skilled craftsmanship.
Care and Longevity Considerations
Proper care and maintenance of hippie wool jumpers require understanding of natural fiber properties and traditional garment care methods. Unlike synthetic alternatives, wool jumpers demand careful washing, drying, and storage practices to maintain their appearance and structural integrity over time.
The longevity potential of well-made hippie wool jumpers far exceeds that of typical fashion garments. With proper care, these pieces can remain functional and attractive for decades, often improving with age as the wool develops a unique patina and character. This durability aligns perfectly with sustainable fashion principles and provides excellent value for conscious consumers.
Conclusion
The hippie wool jumper represents far more than a fashion trend or nostalgic throwback to the 1960s counterculture movement. It embodies enduring values of sustainability, craftsmanship, and cultural authenticity that resonate powerfully in today’s world. As consumers become increasingly aware of fashion’s environmental and social impacts, the principles underlying the hippie wool jumper—support for traditional crafts, preference for natural materials, and appreciation for quality over quantity—offer a compelling alternative to fast fashion culture.
The continued relevance of the hippie wool jumper demonstrates how authentic cultural artifacts can transcend their original context to address contemporary concerns and values. Whether worn as a statement of environmental consciousness, appreciation for traditional crafts, or simply as a comfortable and distinctive garment, the hippie wool jumper continues to serve as a bridge between past wisdom and present needs. Its enduring appeal suggests that the values it represents—sustainability, authenticity, and respect for traditional skills—will remain relevant for generations to come, ensuring that this iconic garment maintains its place in both fashion history and contemporary wardrobes.